How to Choose the Best Solution for Precision Motion Systems
Mar 07, 2025
As the core transmission component in industrial automation and precision equipment, the selection of linear guides is directly related to the accuracy, efficiency, life and stability of the equipment. This article will provide engineers with a systematic selection reference from the aspects of selection principles, key parameters, steps and precautions, combined with actual application scenarios.
Analysis of key parameters before selection
1. Load capacity and direction
Load type: It is necessary to clarify the static load (vertical and lateral force) and dynamic load (inertia force caused by acceleration) borne by the equipment.
Load direction: Linear guides can usually withstand four-way loads, but the raceway layout and slider distribution of the guides need to be selected according to the actual force direction.
Torque balance: The center of gravity position and torque need to be calculated in complex applications to avoid deformation or shortened life of the guides due to uneven force.
2. Accuracy level
Select ordinary level (±50μm), precision level (±10μm) or ultra-high precision level (±5μm) according to application requirements. For example, semiconductor equipment requires nanometer-level positioning accuracy, and ultra-high precision guides should be selected.
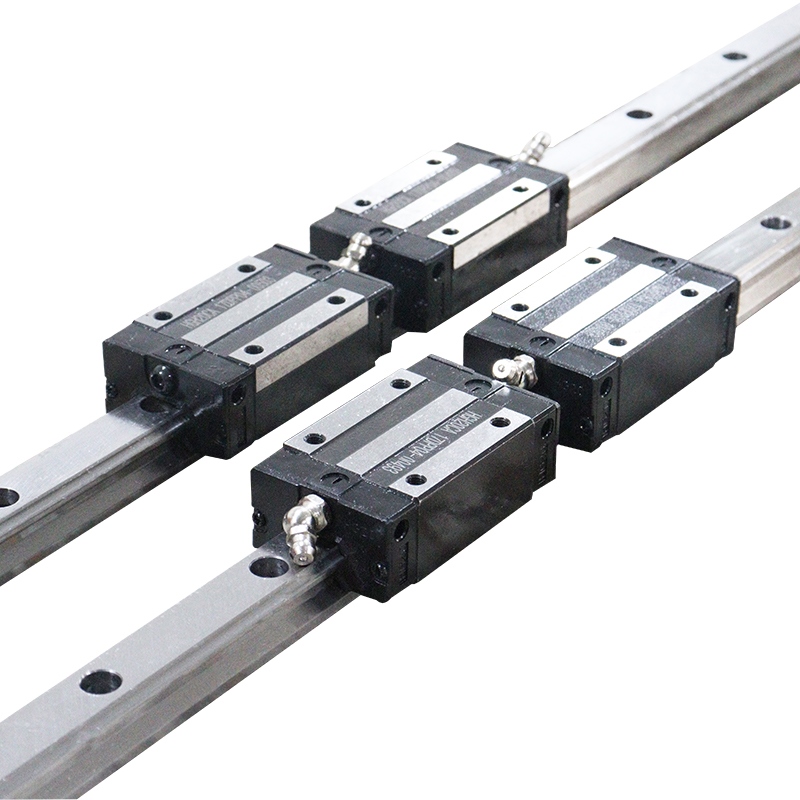
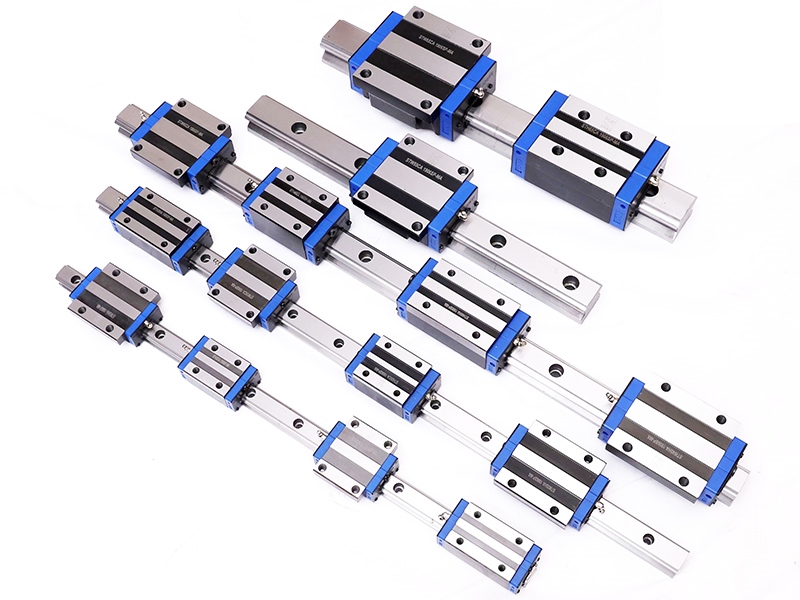
3. Guide type and material
Type selection:
Rolling guide (ball/roller): low friction, high speed, suitable for high-speed processing and precision positioning.
Sliding guide: strong load-bearing capacity, suitable for heavy-load and low-speed scenarios.
Material adaptation:
Carbon steel: high load-bearing, suitable for heavy industry;
Stainless steel: corrosion-resistant, suitable for humid or corrosive environments;
Aluminum alloy: lightweight, suitable for medical equipment or light-load scenarios.
4. Environmental adaptability
Environments such as high temperature, humidity, dust or corrosive media require high-temperature resistant coatings, sealed dustproof designs or special lubrication solutions.
Linear guide selection steps
1. Clear requirements
Determine the movement speed, acceleration, stroke length and installation space limit of the equipment28.
2. Calculate load and life
Calculate the load capacity of the guide according to the load formula (such as static rated load and dynamic rated load), and refer to the life calculation formula provided by the manufacturer (such as rated life L10) to evaluate the maintenance cycle.
3. Select guide specifications
Guide width: The wider the width, the stronger the rigidity and load capacity. Common specifications are 15mm to 45mm.
Preload level: no preload, light preload, medium preload or heavy preload. The higher the preload, the stronger the rigidity, but the friction resistance increases.
4. Lubrication and maintenance design
Choose a centralized lubrication or self-lubricating system, clean dust regularly and add grease to reduce wear.
Typical application scenarios and selection cases
1. CNC machine tools
Requirements: high repeatability (±5μm), high rigidity.
Selection: Ultra-high precision roller guide, carbon steel, heavy preload design, with closed-loop feedback system.
2. Industrial robot
Requirements: flexible movement with multiple degrees of freedom, resistance to frequent start and stop.
Selection: low friction ball guide, stainless steel, dustproof sealing structure.
3. Semiconductor equipment
Requirements: nano-level positioning, resistance to clean room environment.
Selection: air-floating guide or magnetic suspension guide, ultra-high precision grade, dust-free lubrication solution.
Common misunderstandings and precautions in selection
Ignoring the impact of dynamic load: only considering static load may cause the guide to fail due to inertial force overload during high-speed movement.
Excessive pursuit of high precision: Using ultra-high precision guides in non-precision scenarios will increase costs, and ordinary grades can meet the needs.
Insufficient environmental adaptation: Failure to select protective design for dust or corrosive environments will greatly shorten the life of the guide.
Improper installation and maintenance: Inadequate preload adjustment or lack of lubrication will directly affect motion accuracy and stability.
Summary
The selection of linear guides needs to comprehensively consider multiple factors such as load, accuracy, environment, cost, etc., and flexibly adjust them according to the actual application scenarios. Through scientific calculation, reasonable matching parameters and regular maintenance, the performance of the guides can be maximized and the life of the equipment can be extended. It is recommended to fully communicate with suppliers and engineers at the beginning of the selection, and use professional tools (such as load calculation software) to optimize the solution to ensure a balance between efficiency and reliability.
If you need to know more about specific model parameters or application cases, you can refer to the selection manual or technical documents provided by the manufacturer.




 Network Supported
Network Supported